Introduction
The Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) is a crucial economic indicator that measures the health of the manufacturing sector. It provides insights into business conditions and economic trends. Understanding the PMI calculation is essential for interpreting its impact on the economy.
Today’s given signal : https://t.me/calendarsignal/10302
Purchasing Managers’ Index calculation
- There are a number of qualitative questions that determine the PMI. New orders, output, business expectations, and employment are measured and rated by executives from a fairly big sample of companies, amounting to hundreds.
- According to official data, purchasing managers in each country are carefully selected and designed to accurately reflect the true structure of the chosen sector of the economy.
- The survey panels are therefore miniature replicas of the actual economy. Each response is also weighed according to the size of the company and the relative importance of the sector in which it operates in the survey database.
PMI Calculation Variables
- Domestic as well as international investors observe the PMI monthly. A monthly PMI release consists of two parts: the headline PMI value, which provides a snapshot of the economy, and the subindices, which provide data at the component level. As well as providing insights into key economic drivers, sub-indices also provide insight into employment, inflation, exports, and inventories.
- There are five components of the PMI with equal weights: New Orders (30%), Output (25%), Employment (20%), Suppliers’ Delivery Times (15%), Stock of Items Purchased (10%).
- As a result of the following calculations, the Purchasing Managers’ Index is calculated:
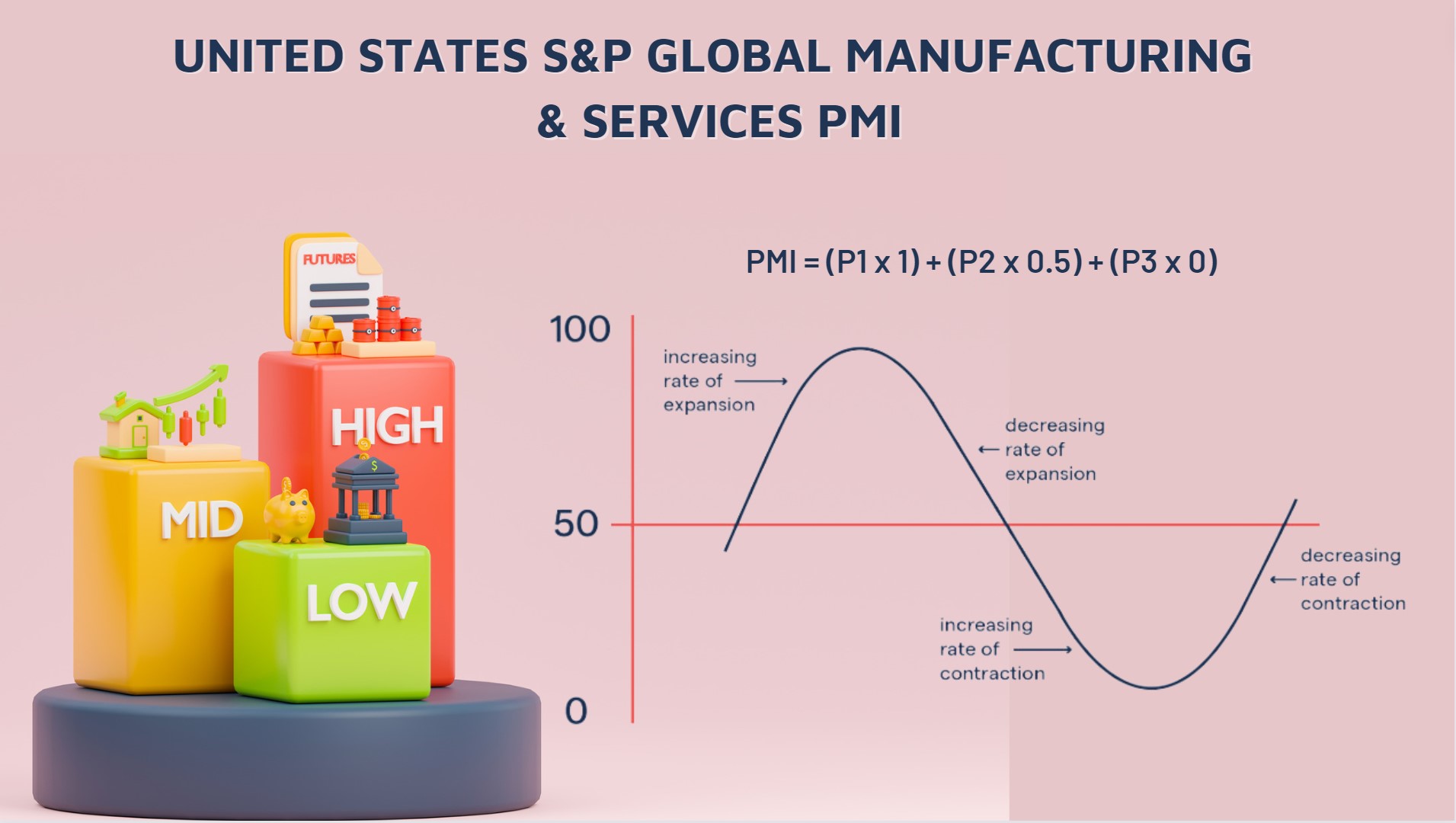
- In general, PMI is defined as (P1 * 1) + (P2 * 0.5) + (P3 * 0)
where:
- P1 = Percentage of answers reporting an improvement.
- P2 = Percentage of answers reporting no change.
- ·P3 = Percentage of answers reporting deterioration.
- The index would be 100.0 if 100% reported an improvement. A zero index would result from 100% reporting a deterioration. The index would be 50.0 if 100% of the panel saw no change (P2 * 0.5).
PMI numbers: how do you read them?
- PMI = 50 indicates no change in business activity. Either all respondents reported no change or an equal number of respondents reported an improvement and deterioration, resulting in a PMI index of 50.
- PMI > 50 indicates expansion/improvement in business activity.
- PMI < 50, denotes contraction/deterioration in business activity.The greater the difference from 50, the greater the expansion or contraction. The rate A comparison of the PMI with the previous month’s data can also reveal the rate of expansion.
- A higher PMI indicates a faster pace of economic growth than the previous month. It is growing at a slower rate if it is lower than the previous month
- The general economy should expand if manufacturing is expanding. Thus, it provides a good indication of the future growth rate of the economy. As a result of reading the PMI report, many economists will adjust their GDP estimates.
PMI’s key benefits
- Timeliness : PMI data are published monthly before comparable official economic data
- Comparability : Using standardized data, compare economies
- Factual sources : Rather than using opinions or confidence-based measurements, use actual business data.
- Extensive coverage : More than 26,000 companies across 40 developed and emerging economies are surveyed monthly
Previous released data results :
Where to contact us :
Website : www.forextrade1.co
Twitter : www.twitter.com/forextrade11
Telegram : telegram.me/ftrade1
Facebook : www.facebook.com/Forextrade01
Instagram : www.instagram.com/forextrade1
YouTube : www.youtube.com/ForexTrade1
Skype : forextrade01@outlook.com
Email ID : info.forextrade1@gmail.com
Discord : https://discord.gg/vEk98ZvrHP
LinkedIn : https://www.linkedin.com/company/forextrade11